

axSpAに関する最初の展示にいく
axSpAの病理生物学を探る
axSpAの慢性炎症の病因は 複雑で、多因子性であり、外的要因から生じる。1-3
….複数の獲得免疫細胞および自然免疫細胞と炎症誘発性サイトカインが関与している。1-3


Iain MCINNES教授の講義シリーズ
サイトカインとリウマチ学の進歩を理解する
著名なリウマチ学の研究者であり、臨床医でもあるIain McInnes教授の講義シリーズ第1弾のビデオをご視聴いただき、分子医学の進歩がaxSpAの病態理解にどのような変革をもたらしたか、ご確認ください。
axSpAに至る病態
axSpAに至る病態はまだ完全には解明されていない。しかし、最近の研究により、さまざまな臨床症状・徴候を引き起こす炎症の開始と維持に関与する経路、およびそれに関与する主要な獲得免疫細胞や自然免疫細胞、サイトカインに関する知見が明らかになってきている。1,3-7
炎症を引き起こすサイトカインの役割
最新のエビデンスによると、IL-17A、IL-17F、TNF、IL-12、IL-23などのサイトカインや、JAK/STAT経路の直接的または間接的な関与が、SpAのさまざまな組織における炎症の促進において、それぞれ異なる役割を担っている。それぞれの相対的な寄与は複雑であるが、どのサイトカインがさまざまな臨床症状・徴候やSpAの疾患表現型に寄与するかについて、重要な区別が生まれつつある。3-5,7,8
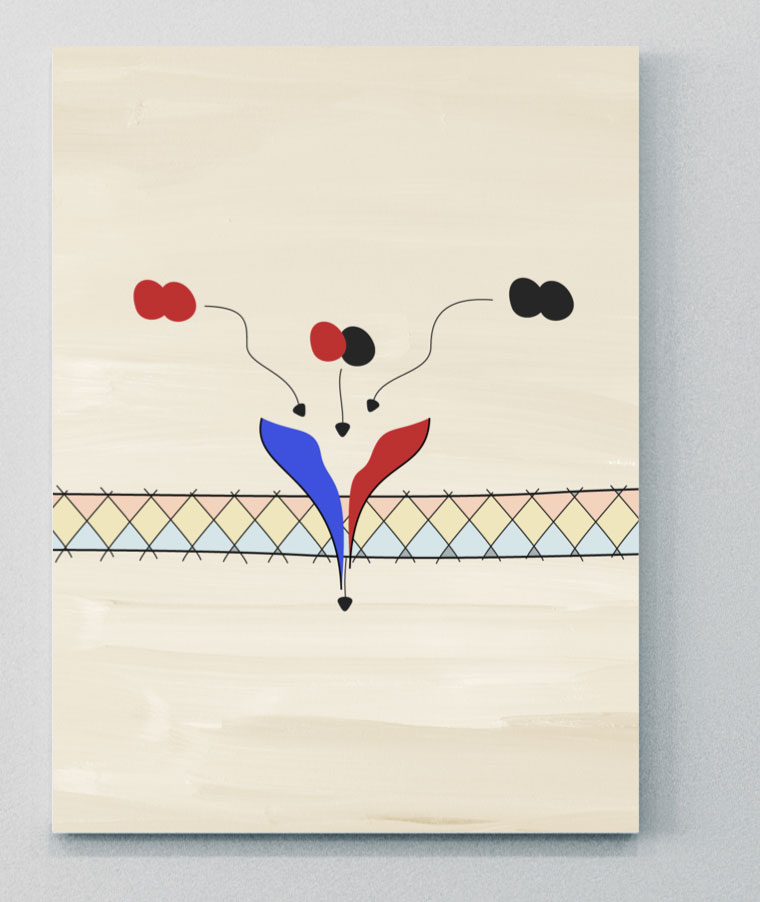


IL-17ファミリー
IL-17サイトカインファミリーは、IL-17A、IL-17B、IL-17C、IL-17D、IL-17E、およびIL-17Fを含む6つのメンバーで構成されている。9,13
IL-17AとIL-17Fは~50%の構造的相同性を共有し、同様の炎症誘発機能を持ち、同じ受容体複合体を介してシグナルを伝達する。12 IL-17AとIL-17Fはホモ二量体およびヘテロ二量体として存在する。つまり、3つのサイトカイン(IL-17A/A、IL-17A/F、IL-17F/F)が存在しており、これらすべてはaxSpAの炎症に寄与することが示されている。12,14
IL-17受容体ファミリーには5つのメンバーがある。2つのIL-17受容体(IL-17RCとIL-17RA)が協調して働き、IL-17A/A、IL-17F/F、IL-17A/Fによるシグナル伝達を媒介すると考えられている。1,13
IL-17AとIL-17Fは、TNFのような他の炎症性メディエータと協力して、炎症反応を増幅することが研究で示されている。12 病的な骨形成に対するIL-17AとIL-17Fの寄与は、骨形成分化のヒト骨膜由来幹細胞モデルにおいて示されており、骨病変におけるIL-17AとIL-17Fの重要性を示している。10
受容体複合体


Iain McInnes教授の講義シリーズ
axSpAの病態におけるIL-23-IL-17軸の役割について理解する
Iain McInnes教授と一緒に、axSpAの炎症性サイトカイン反応促進におけるIL-23-IL-17軸の重要な最新知見に迫りましょう。
エビデンスによると、axSpAでは、IL-17はIL-23依存経路とIL-23非依存経路によって制御されていることを示唆する
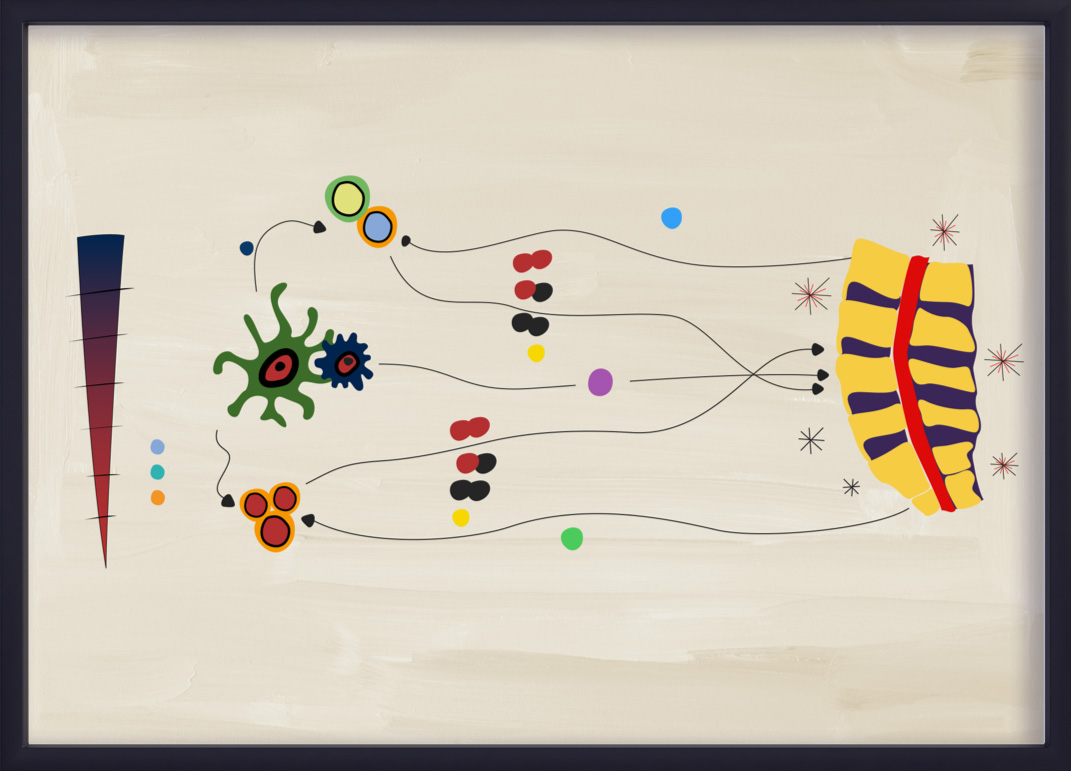
IL-23–IL-17軸プロセスについて
IL-23は、Th17細胞からのIL-17AとIL-17Fの産生を含むTh17サブセットの増殖と生存を促進する役割を担っている。このプロセスは一般にIL-23–IL-17軸と呼ばれ、axSpAを含むいくつかの炎症性疾患に関与している。13,14,18,19
最近のエビデンスによると、IL-23–IL-17軸はaxSpAでは直線的な「カスケード」ではない。IL-23とIL-17は、部分的には重複しているが、異なる生物学と病理生物学を示している。20 IL-23-IL-17獲得免疫経路は依然としてaxSpAの炎症を促進する役割を果たしていると考えられているが、自然免疫系の細胞もIL-23とは無関係にIL-17AとIL-17Fを産生する。18,20 axSpAの病理生物学のこの側面は、IL-23–IL-17軸が疾患において依然として重要な役割を果たしているように見えるPsAとは異なるかもしれない。4,19-21
IL-23を阻害する生物学的製剤の臨床試験では優位性を見いだせなかったため、axSpAの病理生物学におけるこのサイトカインの役割は不明。
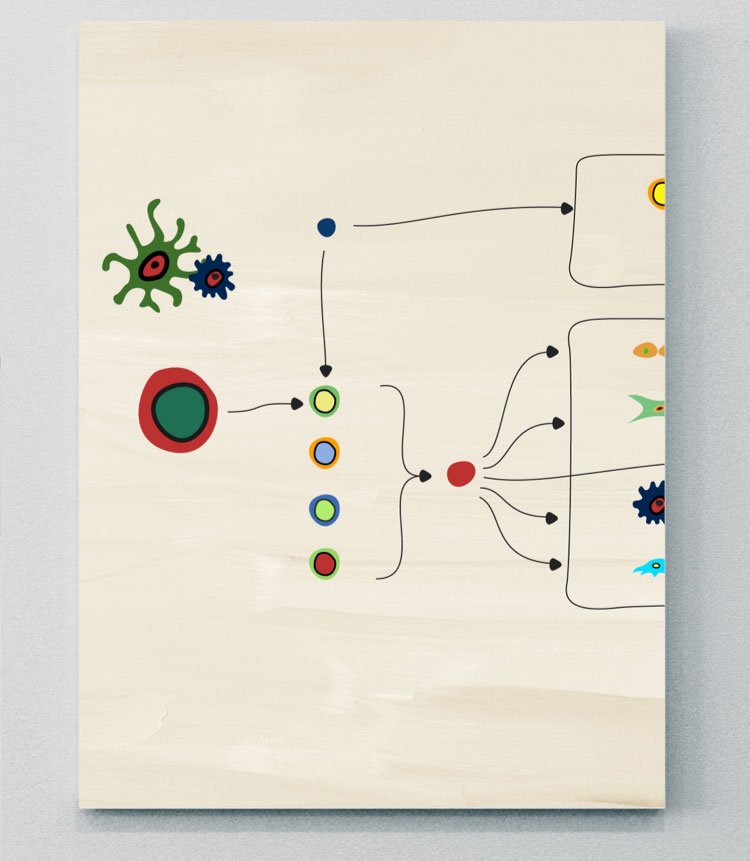
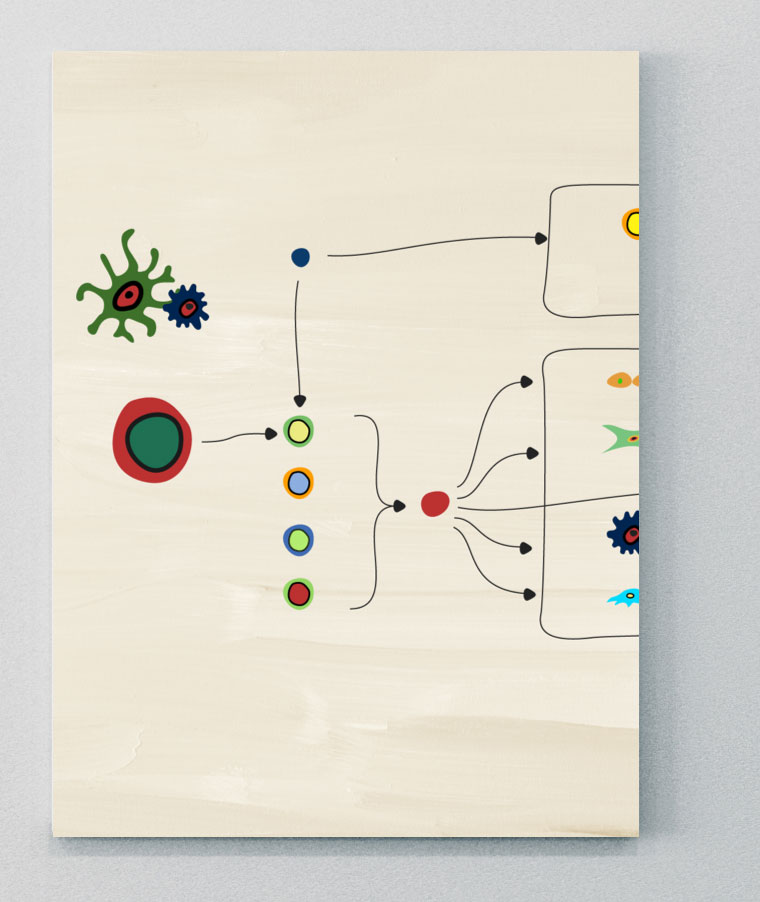
IL-23
IL-17の重要な上流制御因子13,20
IL-23 はIL-12スーパーファミリーの一つであり、p40鎖とp19鎖からなるヘテロ二量体である。13,20乾癬、PsA、axSpA、IBDを含む いくつかの免疫介在性炎症性疾患の発症に関与する重要なサイトカインである。20しかしながら、異なる細胞や下流のサイトカイン経路との相互作用は、疾患によって異なる可能性がある。20
樹状細胞が活性化された腸や皮膚のようなバリア部位からIL-23が移動し、axSpAにおける疾患発症部位に移動できることを示すエビデンスもあるが、これについてはさらに調査する必要がある。20IL-23の重要な炎症誘発作用は、IL-17、IL-22、TNFを産生するTh17細胞の刺激であり、炎症、骨形成、骨びらんを引き起こす。4,13,20
歴史的に、IL-23-IL-17軸はSpA疾患における病的な骨形成を推進する中心的な要素であるとみなされてきたが、エビデンスが進展するにつれて、骨量減少や骨形成につながる病態は、異なる骨部位や異なる病型で異なる可能性があることが明らかになってきている.4,20
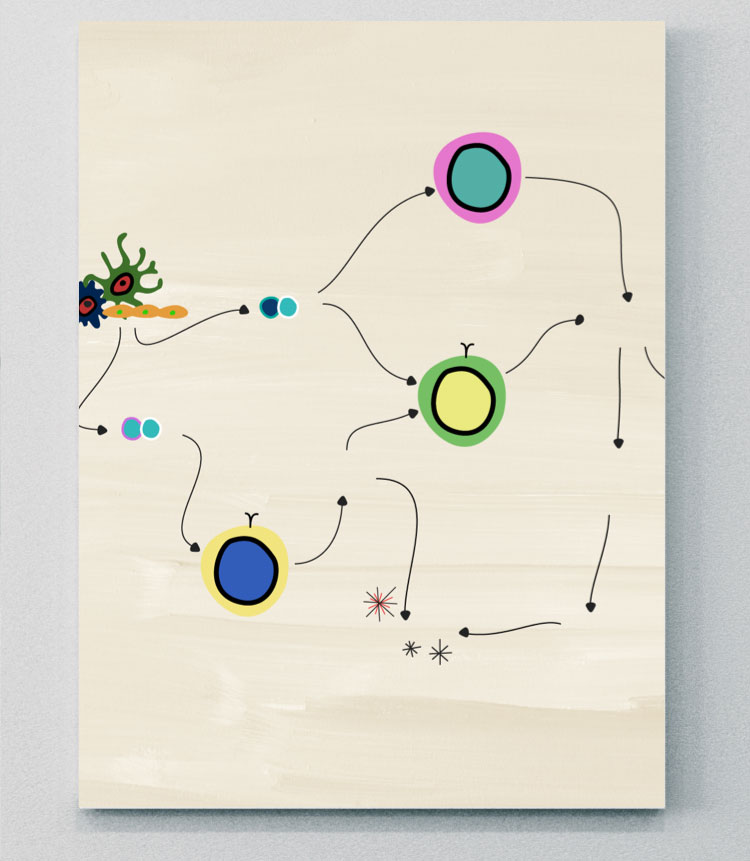
IL-12
axSpAにおけるIL-12の役割
IL-12は2つのサブユニット(p35とp40)からなる炎症誘発性サイトカインで、活性型ヘテロ二量体p70を形成する。24 自然免疫細胞によって産生され、ナイーブT細胞からIFN-γ 産生Th1細胞 への分化を誘導し、T細胞の疲弊を防ぐ。24,25
IL-12とIL-23の活性は密接に関連している。これらの炎症性サイトカインはどちらもp40サブユニットと受容体鎖(IL-12R1)を共有しており、それぞれ異なるIL-12とIL-23のシグナル伝達経路を制御している。24
axSpAでは、IL-12とIL-23の過剰活性化により、循環しているTh1とTh17細胞の数が増加する。これにより、サイトカインやタンパク質からのシグナル伝達が活性化され、単球から破骨細胞への分化が促進され、仙腸関節や末梢関節の損傷につながる。1,26,27
IL-12を阻害する生物学的製剤の臨床試験では優位性を見いだせなかったため、axSpAの病理生物学におけるこのサイトカインの役割は不明。

TNF
TNFシグナル伝達はaxSpAの病態に関与している
TNFスーパーファミリー(TNFSF)は、構造的に関連する19の多面作用性サイトカインから構成されている。29,30 TNFSFタンパク質は、炎症の主要な促進因子であり、アポトーシス、血管形成、細胞増殖、その他の重要な生物学的機能の調節に関与している。29
TNF-α は、膜貫通型と可溶型があり、主にT細胞、NK細胞、マクロファージによって作られる。31TNF-α細胞シグナル伝達は2つの受容体、TNF 受容体1(TNFR1)とTNFR2を通して起きるが、これらの細胞シグナル伝達 のメカニズム、リガンド親和性、発現パターンは異なっている。32,33TNFR1は炎症性免疫と自然免疫反応に関与する支配的な受容体である。28
TNFが介在する炎症誘発性TNFR1シグナルは、破骨細胞形成とマトリックスメタロプロテアーゼ産生によって脊椎の異化性骨吸収を亢進させ、骨びらんを引き起こす。28さらに、TNFR1およびTNFR2シグナル伝達は(他のサイトカインの関与とともに)、骨芽細胞活性の亢進を通じて、脊椎の癒合を示す病的な骨形成をもたらす可能性がある。28
axSpAでは、TNFを介したシグナル伝達が疾患の進行に重要な役割を果たしている。
活性化した樹状細胞はTNF-αを分泌し、T細胞シグナル伝達とTh細胞の分化を促進する。30TNFの上昇レベルは、滑膜や、前部ぶどう膜炎患者の漿液や房水のような体の他の場所で見られる。34
axSpAでは、TNFはIL-17およびIL-23経路と相乗的に作用する
- IL-23はTh17細胞の分化を刺激し、IL-17などのサイトカインの産生を引き起こし、TNFのさらなる亢進を引き起こす。1
- IL-17はTNFと結合することができ、どちらかのサイトカインが単独で作用するよりも強い炎症誘発性サイトカイン(IL-6やIL-8など)の発現を引き起こす。35
TNF=腫瘍壊死因子。

JAK-STAT
JAK-STAT経路はaxSpAの病態に重要な役割を果たしている可能性がある。
JAK分子は細胞内チロシンキナーゼの一群で、4つのアイソフォームを構成する:JAK1、JAK2、JAK3、TYK2。37これらのグループは シグナル転写因子および転写活性化因子(STAT)分子と結合している。5多くの免疫細胞とエフェクター分子は、JAK分子とSTAT分子の異なる組み合わせを用いて、細胞表面から核へのシグナルを変換し、そこで転写を活性化し、遺伝子の活性化を誘導する。この下流の遺伝子の活性化は、axSpAにおける病態の活性化を含む、さまざまな生物学的プロセスを制御する役割を担っている。5,36,38多くのSpA関連サイトカインは、直接的または間接的にJAK-STAT経路を媒介する。36
JAK=ヤヌスキナーゼ
科学アニメーションシアターを見る
TNF、IL-17A、IL-17F、IL-23の役割など、SpAを引き起こすメカニズムを解明する

数種類のサイトカインが、axSpAにおける炎症の促進において、それぞれ異なる役割を担っていることを探求する


病理生物学に関する次の展示室
免疫調節異常
サイトカイン調節異常がaxSpAにおける炎症を引き起こす仕組みを探る。
axSpAおよびPsAに関する詳しい情報については、UCBCares® Rheumatologyに登録してください
- Furst DE, Louie JS. Targeting inflammatory pathways in axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):135. Published 2019. doi:10.1186/s13075-019-1885-z
- Watad A, Bridgewood C, Russell T, et al. The early phases of ankylosing spondylitis: emerging insights from clinical and basic science. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2668. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02668
- Rezaiemanesh A, Abdolmaleki M, Abdolmohammadi K, et al. Immune cells involved in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;100:198-204. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.108
- McGonagle DG, McInnes IB, Kirkham BW, et al. The role of IL-17A in axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: recent advances and controversies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1167–1178
- Hammitzsch A, Lorenz G, Moog P. Impact of janus kinase inhibition on the treatment of axial spondyloarthropathies. Front Immunol. 2020;11:591176. Published 2020. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.591176
- Schwartzman S, Ruderman EM. A road map of the axial spondyloarthritis continuum. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022 Jan;97(1):134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.08.007.
- Rosine N, Miceli-Richard C. Innate cells: the alternative source of IL-17 in axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis?. Front Immunol. 2021;11:553742. Published 2021. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.553742
- Siebert S, Millar NL, McInnes IB. Why did IL-23p19 inhibition fail in AS: a tale of tissues, trials or translation? Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(8):1015-1018. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213654
- Yang XO, Chang SH, Park H, et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses by IL-17F. J Exp Med. 2008;205(5):1063-1075. doi:10.1084/jem.20071978
- Shah M, Maroof A, Gikas P, et al. Dual neutralisation of IL-17F and IL-17A with bimekizumab blocks inflammation-driven osteogenic differentiation of human periosteal cells. RMD Open. 2020;6(2):e001306. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001306
- Goepfert A, Lehmann S, Blank J, et al. Structural analysis reveals that the cytokine IL-17F forms a homodimeric complex with receptor IL-17RC to drive IL-17RA-independent signaling. Immunity. 2020;52(3):499-512.e5. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.02.004
- Glatt S, Baeten D, Baker T, et al. Dual IL-17A and IL-17F neutralisation by bimekizumab in psoriatic arthritis: evidence from preclinical experiments and a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial that IL-17F contributes to human chronic tissue inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(4):523-532. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212127
- Tsukazaki H, Kaito T. The role of the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6401. Published 2020. doi:10.3390/ijms21176401
- Bridgewood C, Sharif K, Sherlock J, et al. Interleukin-23 pathway at the enthesis: The emerging story of enthesitis in spondyloarthropathy. Immunol Rev. 2020;294(1):27-47. doi:10.1111/imr.12840
- Blanco P, Palucka AK, Pascual V, Banchereau J. Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19(1):41-52. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.10.004
- Cole S, Murray J, Simpson C, et al. Interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 synergize to promote MAIT Cell IL-17A and IL-17F production independently of IL-23 signaling. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585134. Published 2020. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.585134
- Russell T, Watad A, Bridgewood C, et al. IL-17A and TNF modulate normal human spinal entheseal bone and soft tissue mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis, adipogenesis, and stromal function. Cells. 2021;10(2):341. Published 2021. doi:10.3390/cells10020341
- McGonagle D, Watad A, Sharif K, et al. Why inhibition of IL-23 lacked efficacy in ankylosing spondylitis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:614255. Published 2021. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.614255
- Taams LS, Steel KJA, Srenathan U, et al. IL-17 in the immunopathogenesis of spondyloarthritis. Nat Rev Rheum. 2018;14(8):453–466. Published 2018. doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0044-2
- Mease P, Van den Bosch F. IL-23 and axial disease: do they come together? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(Suppl 4):iv28-iv33. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab617
- Baeten D, Adamopoulos IE. IL-23 Inhibition in ankylosing spondylitis: where did it go wrong?. Front Immunol. 2021;11:623874. Published 2021. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.623874
- Boutet MA, Nerviani A, Gallo Afflitto G, et al. Role of the il-23/il-17 axis in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: the clinical importance of its divergence in skin and joints. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):530. Published 2018. doi:10.3390/ijms19020530
- Zhu W, He X, Cheng K, et al. Ankylosing spondylitis: etiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Bone Res. 2019;7:22. doi: 10.1038/s41413-019-0057-8.
- Schurich A, Raine C, Morris V, et al. The role of IL-12/23 in T cell-related chronic inflammation: implications of immunodeficiency and therapeutic blockade. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(2):246-254. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kex186
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a pro-inflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:251-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.001343
- Poddubnyy D, Jadon DR, Van den Bosch F, et al. Axial involvement in psoriatic arthritis: An update for rheumatologists. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(4):880-887. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.06.006
- Chyuan IT, Lai JH. New insights into the IL-12 and IL-23: From a molecular basis to clinical application in immune-mediated inflammation and cancers. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;175:113928. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113928
- Lata M, Hettinghouse AS, Liu CJ. Targeting tumor necrosis factor receptors in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1442(1):5-16. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13933
- Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Kim JH. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood. 2012;119(3):651-665. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-325225
- Croft M, Siegel RM. Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(4):217-233. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2017.22
- Jang DI, Lee AH, Shin HY, et al. The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in autoimmune disease and current TNF-α inhibitors in therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22;2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052719
- Holbrook J, Lara-Reyna S, Jarosz-Griffiths H, et al. Tumour necrosis factor signaling in health and disease. F1000Res. 2019; 8:F1000 Faculty Rev-111. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.17023.1
- Mantravadi S, Ogdie A, Kraft WK. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10(8):899-910. doi:10.1080/17512433.2017.1329009
- Ebrahimiadib N, Berijani S, Ghahari M, et al. Ankylosing spondylitis. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021;16(3):462-469. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v16i3.9440
- Noack M, Beringer A, Miossec P. Additive or synergistic interactions between IL-17A or IL-17F and TNF or IL-1β depend on the cell type. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1726. Published 2019. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01726
- McInnes IB, Szekanecz Z, McGonagle D, et al. A review of JAK-STAT signaling in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis and the role of JAK inhibition [published online ahead of print, 2021 Oct 20]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab740. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab740
- White JPE, Coates LC. JAK1 selective inhibitors for the treatment of spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(Suppl 2): ii39-ii44. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa815
- Fragoulis GE, McInnes IB, Siebert S. JAK-inhibitors. New players in the field of immune-mediated diseases, beyond rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(Suppl 1):i43-i54. Published 2019. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key276